SSH proxy with PuTTY#
Warning
If you simply want to configure PuTTY to connect to the login node of a VSC cluster, this is not the page you are looking for. Please check out Terminal using PuTTY.
Rationale#
The SSH protocol provides a safe way of connecting to a computer, encrypting traffic and avoiding passing passwords across public networks where your traffic might be intercepted by someone else. Yet making a server accessible from all over the world makes that server very vulnerable. Therefore servers are often put behind a firewall, another computer or device that filters traffic coming from the internet.
All VSC clusters are behind a firewall, which is configured by default to block all traffic from abroad. That is why if you are accessing the VSC clusters from abroad, it is necessary that you first authorize your own connection on the VSC Firewall.
Another example are the compute nodes of the HPC cluster. You can (usually) directly connect to the login nodes of the cluster, but compute nodes are not reachable from outside. In that case you can only open a connection to a compute node from your computer by using the login node as proxy.
Note
Connections to compute nodes are restricted to users with active jobs on those nodes.
This all sounds quite complicated, but once things are configured properly it is really simple to log on to the host.
Setting up a proxy in PuTTY#
Warning
In the screenshots below we show the proxy setup for user vscXXXXX to
the login.muk.gent.vsc login node for the muk cluster at UGent
via the login node vsc.login.node.
You will have to
replace
vscXXXXXwith your own VSC accountreplace
login.muk.gent.vscby the node that is behind a a firewall that you want to accessreplace
vsc.login.nodewith the name of the login node of the VSC cluster you want to use as a proxy, which can be found in the cluster description on Tier-1 Infrastructure or Tier-2 Infrastructure
Setting up the connection in PuTTY is a bit more complicated than for a simple direct connection to a login node.
First you need to start up pageant and load your private key into it. See the instructions on using Pageant.
In PuTTY, go first to the “Proxy” category (under “Connection”). In the Proxy tab sheet, you need to fill in the following information:
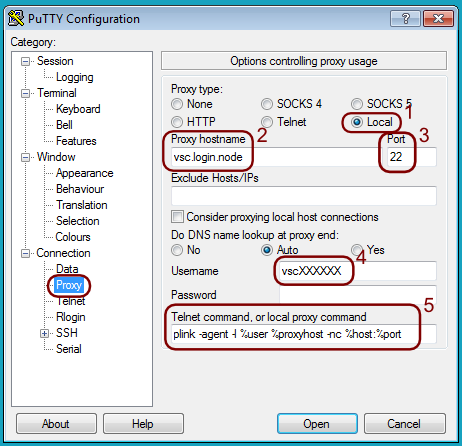
Select the proxy type: “Local”
Give the name of the proxy server. This is your usual VSC login node, with a hostname of the form
login.hpc.<institute>.be, and not the computer on which you want to connect to.Make sure that the “Port” number is 22.
Enter your VSC-id in the “Username” field.
In the “Telnet command, or local proxy command”, enter the string
plink -agent -l %user %proxyhost -nc %host:%port
Note
plink(PuTTY Link) is a Windows program and comes with the full PuTTY suite of applications. It is the command line version of PuTTY. In case you’ve only installed the executables putty.exe and pageant.exe, you’ll need to download plink.exe also from* the PuTTY web site We strongly advise to simply install the whole PuTTY-suite of applications using the installer provided on the PuTTY download site.
Now go to the “Data” category in PuTTY, again under “Connection”.
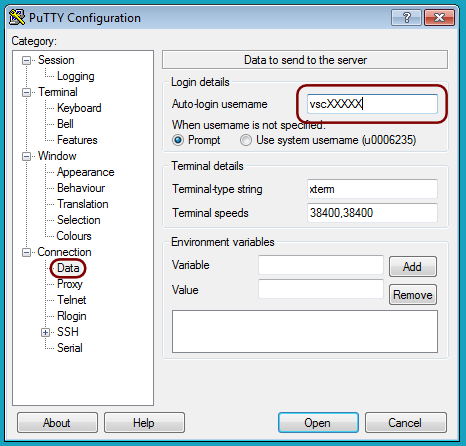
Fill in your VSC-id in the “Auto-login username” field.
Leave the other values untouched (likely the values in the screen dump)
Now go to the “Session category
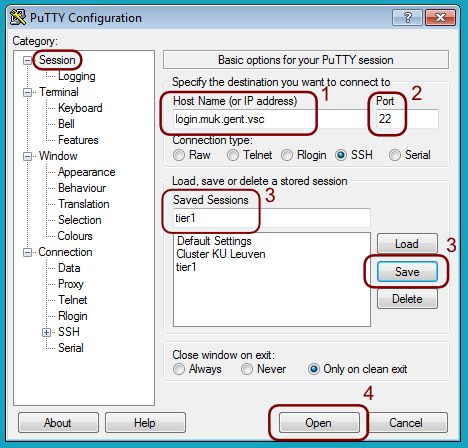
Set the field “Host Name (or IP address) to the computer you want to log on to. If you are setting up a proxy connection to access a computer on the VSC network. you will have to use its name on the internal VSC network.
Make sure that the “Port” number is 22.
Finally give the configuration a name in the field “Saved Sessions” and press “Save”. Then you won’t have to enter all the above information again.
And now you’re all set up to go. Press the “Open” button on the “Session” tab to open a terminal window.
For advanced users#
If you have an X-server on your Windows PC, you can also use X11 forwarding and run X11-applications on the host. All you need to do is click the box next to “Enable X11 forwarding” in the category “Connection” -> “SSH”-> “X11”.
What happens behind the scenes:
By specifying “local” as the proxy type, you tell PuTTY to not use one of its own build-in ways of setting up a proxy, but to use the command that you specify in the “Telnet command” of the “Proxy” category.
The following command contains templated values that will be replaced by real values depending on your settings
plink -agent -l %user %proxyhost -nc %host:%port
%userwill be replaced by the userid you specify in the “Proxy” category screen%proxyhostwill be replaced by the host you specify in the “Proxy” category screen (vsc.login.node in the example)%hostby the host you specified in the “Session” category (login.muk.gent.vsc in the example) and %port by the number you specified in the “Port” field of that screen (and this will typically be 22).
The plink command will then set up a connection to %proxyhost using
the user ID %user. The -agent option tells plink to use pageant for
the credentials. And the -nc option tells plink to tell the SSH
server on %proxyhost to further connect to %host:%port.
